Tears play an essential role in keeping your eyes healthy, comfortable, and protected. They hydrate your eyes, wash away debris, and help you see clearly. But when something feels off—like a stinging or burning sensation—it can catch you off guard and make everyday moments uncomfortable.
Tears can burn when your eyes are irritated by environmental triggers or underlying issues like dry eye, a common chronic eye condition. Understanding why this happens can help you find relief and protect your long-term eye health with the right care and professional support.
What Are Tears?
Tears aren’t just water running down your face when you’re emotional. They’re actually a complex mixture of water, oils, mucus, and other ingredients your eyes produce constantly—and for good reason.
Your tears help keep your eyes healthy, comfortable, and functioning properly. And depending on the situation, your body makes different types of tears using slightly different ingredients.
Let’s explore how tears work, what they’re made of, and why they sometimes burn your eyes.
How Are Tears Made?
Your tear system—called the lacrimal apparatus—does more than just create tears. It also helps distribute and drain them.
Tears begin in the tear glands (lacrimal glands) located above your eyes. These glands mix water and salt to create the base of your tears. At the same time, the meibomian glands, which line your eyelids, produce oils that blend with the water to create a protective, balanced tear film.
Once your tears do their job, they need to drain away. This happens through tiny openings in the corners of your eyes called lacrimal puncta. Every time you blink, old tears are pushed into these openings. From there, the tears travel to the lacrimal sacs and then down the tear ducts, where they eventually drain into the nose.
The 3 Types of Tears
Your body produces 3 types of tears, each with a different role:
1. Basal Tears
These are the everyday tears that constantly coat your eyes. They form a protective barrier, keep the surface of your eyes moist, and provide nutrients to the cornea.
2. Reflex Tears
These tears are triggered when your eyes encounter irritants like dust, smoke, or onion fumes. Reflex tears tend to have higher levels of antibodies, helping to flush out harmful particles and bacteria.
3. Emotional Tears
These are the tears that appear when you’re feeling joy, sadness, pain, or frustration. While they don’t protect your eyes in the same way, they can serve as an important emotional release and social signal.
What Are Tears Made Of?
No matter the type, all tears share a basic structure made of three layers:
- Mucus layer (closest to the eye): Helps the tear film stick to the eye’s surface.
- Water layer (middle): Keeps the eye hydrated and protects the cornea.
- Oil layer (outermost): Prevents evaporation and helps spread the tear evenly across the eye.
Depending on their purpose, tears also contain:
- Salts & electrolytes for balance
- Antibodies to fight infection
- Nutrients to nourish the eye
- Hormones—especially in emotional tears, which may explain the calming feeling after a good cry
Each of these ingredients helps tears do their specific job, whether that’s protecting, hydrating, or expressing emotion.
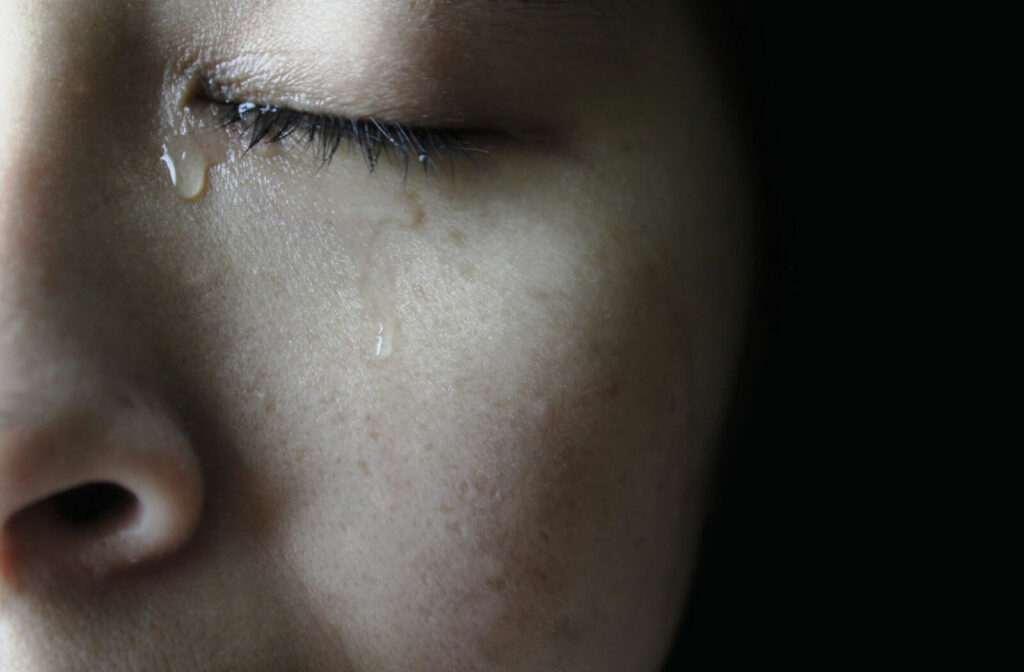
Why Do Tears Sometimes Burn?
If you’ve ever cried or blinked through watering eyes and felt a burning or stinging sensation, it’s usually due to irritation. That irritation can come from the environment or from a medical condition.
Environmental Causes
Tears themselves aren’t usually the problem—it’s what’s already irritating your eyes that can make tears feel like they’re burning. Common causes include:
- Dry air (especially from heaters or air conditioners)
- Smoke
- Allergens like pollen or pet dander
- Dust
- Chemical exposure, including cleaning products or chlorine
Sweat can also cause your eyes to burn. When it runs into your eyes—especially if it contains sunscreen, makeup, or skincare products—it can mix with your tear film and lead to irritation.
Medical Causes
If you experience burning tears regularly or alongside other symptoms like redness or swelling, it may point to an underlying eye condition. Possible causes include:
- Dry eye disease: When your eyes don’t produce enough tears—or the right kind—your eyes can become dry and inflamed.
- Blepharitis: Chronic eyelid inflammation can make your eyes feel sore and sensitive.
- Photokeratitis: Also known as a sunburn on your eye’s surface, often from UV exposure without sunglasses.
- Conjunctivitis (pink eye): Inflammation of the clear tissue covering the white part of your eye can lead to burning and discomfort.
When to See Your Optometrist
Occasional burning from environmental triggers is usually nothing to worry about. But if your eyes burn often or you experience other symptoms like itching, redness, or blurry vision, it’s time to talk to your optometrist.
At Vision Care Center, we take the time to understand your symptoms and tailor your care with precision and compassion. Whether it’s dry eye, allergies, or something more complex, our team is here to help you find lasting relief.
Book your next appointment today and let’s keep your eyes feeling clear, comfortable, and protected.