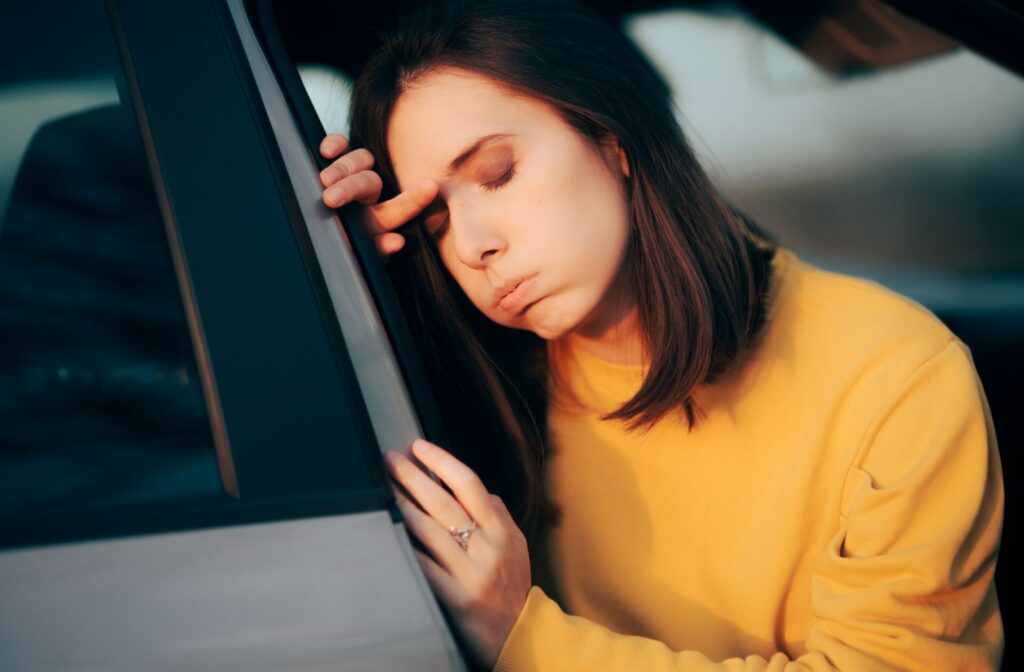
Motion sickness is an unpleasant and bothersome feeling of nausea, dizziness, and fatigue that affects many people when they’re traveling in a vehicle. Whether you are in a car, bus, train, or airplane, motion sickness can strike unexpectedly and ruin your travel experience. This condition is more common than you might think and can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. Surprisingly, misalignment with your eyes could be to blame.
Motion sickness while driving happens when your body sends mixed messages to your brain, confusing it as to whether or not you’re moving. Your optometrist can help determine if your vision is the cause with a comprehensive eye exam.
What Causes Motion Sickness?
Motion sickness happens due to a discrepancy between what the eyes see and what the inner ear senses. Your inner ear is responsible for maintaining your balance and orientation, and it senses the movement of your head and body in space.
However, when you are in a moving vehicle, your eyes may perceive the scenery as stationary, while your inner ear senses the movement of the car, causing confusion and disorientation. This mismatch between what the eyes see and what the inner ear senses leads to motion sickness symptoms, including:
- Cold sweats
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Trouble concentrating
- Irritability
- Increased saliva
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Rapid breathing
It is possible that your body interprets this disagreement between the senses as a sign that you have eaten something dangerous or poisonous. That’s why it’s trying to make you vomit!
Women and children between ages 1–12 are most likely to get motion sickness, and 1 in 3 people have experienced it at some point. It appears that motion sickness can run in families, though other risk factors can include:
- Using hormonal birth control
- Inner ear disorders
- Menstrual periods
- Migraines
- Parkinson’s disease
- Pregnancy
Additionally, some people with binocular vision dysfunction have noted motion sickness while driving.

What is Binocular Vision Dysfunction?
Driving requires an array of visual skills, including depth perception, peripheral vision, and binocular vision, which some people can have difficulty with.
Binocular vision is the ability to use both eyes together as a team to create a single, clear image. When we look at an object, each eye sees it from a slightly different angle, and the brain combines these two images to give a sense of how far away the object is. Binocular vision dysfunction is a condition that affects how the eyes work together, leading to misalignment or eye strain.
The symptoms of binocular vision dysfunction can vary, but one of the most common is eye fatigue. This can make it difficult to focus on the road, leading to blurred or double vision. Other symptoms may include:
- Difficulty seeing in dim lighting
- Light sensitivity
- Trouble judging distances between objects
- Poor hand-eye coordination
- Squinting
- Glares or halos around lighting
- Eyestrain or pain
These symptoms can be particularly acute during long car journeys, increasing the risk of motion sickness while driving.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek a professional diagnosis. An optometrist can carry out a comprehensive eye exam, including tests of visual acuity, eye alignment, and depth perception. Based on the results, we can determine whether you have binocular vision dysfunction or another visual condition.
Vision Therapy for BVD
Vision therapy is a non-invasive way of improving binocular vision dysfunction. It involves a range of exercises and activities designed to improve the balance between the two eyes and how they work together.
For example, a therapist can recommend prism glasses to realign the eye and bring it into the correct position. Other techniques involve balancing exercises, specialized eye muscle exercises, and computer-based activities for eye teaming or tracking. When performed correctly and under the guidance of a trained professional, these techniques can lead to significant improvements in visual function.
While vision therapy is typically prescribed for children, adults can also benefit from this treatment. It’s particularly useful for those who have experienced an injury, surgery, or medical condition that has affected their ability to see properly.
How Long Does Vision Therapy Take?
The duration of vision therapy varies depending on your specific needs and condition. In some cases, a comprehensive program can take several months to a year to complete. Vision therapy is not a one-size-fits-all approach, and each program is specifically tailored to your situation.
It’s crucial to work with a certified specialist or vision therapist.
Quick Remedies for Motion Sickness
Fortunately, you can take steps to reduce or avoid motion sickness while driving. First, try cracking a window, or turning up the fans: the air on your skin is another sign to your body that you really are moving. You can also try:
- Nibbling on crackers
- Drink water or carbonated beverages, but avoid caffeine
- Distract yourself with music or talking
- Take along a ginger or chamomile tea
- Licorice root lozenge
These treatments can have varying effectiveness depending on what is causing your motion sickness, but they’re generally harmless and worth a try if you start to feel the nausea setting in.
Drive Safe & See Clearly
Motion sickness while driving is a common and uncomfortable condition that can ruin your travel experience, but sometimes your optometrist can help! Binocular vision dysfunction can affect you in little ways that you may not notice until they’re unavoidable.
With the proper guidance and support, it’s possible to improve your vision and regain your quality of life. Vision Care Center offers vision therapy for binocular vision dysfunction, providing the necessary tools for children and adults to potentially overcome this condition and see clearly.
If you experience motion sickness while driving, book your appointment today, and let’s discover if your eyes are the problem.